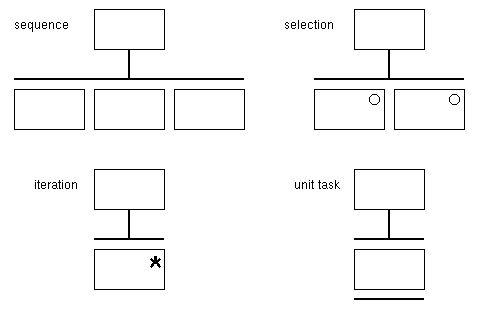
Structure Chart Notation
Task decomposition approach

Structure Chart Notation
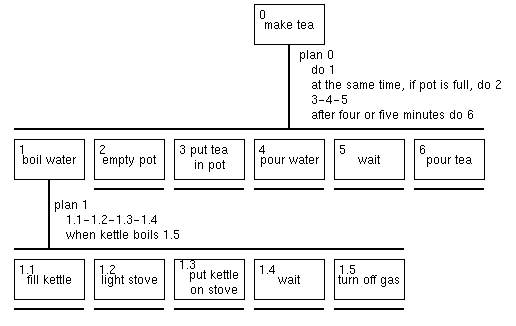
Tea-making Structure Chart
0. make tea
1. boil water
1.1 fill kettle
1.2 light stove
1.3 put kettle on stove
1.4 wait
1.5 turn off stove
2. empty pot
3. put leaves in pot
4. pour water
5. wait
6. pour tea
Plan 0: do 1.
if pot is full,
then do 2 at the same time
do 3-4-5
when tea is brewed, do 6
Plan 1: do 1.1-1.2-1.3-1.4
when water is boiling, do 1.5
Tea-making HTA model in textual notation
Control program for SHAKEY, developed at Stanford Research Institute
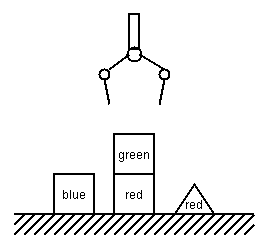
SHAKEY's Blockworld
Early planner - hierarchical plans, constructed bottom-up
HTA constructs plans top-down, but decomposes tasks in a similar way
Knowledge based approach
Psychology of Human Computer Interaction, Card, Moran and Newell, 1983
GOMS is based on the Model Human Processor:
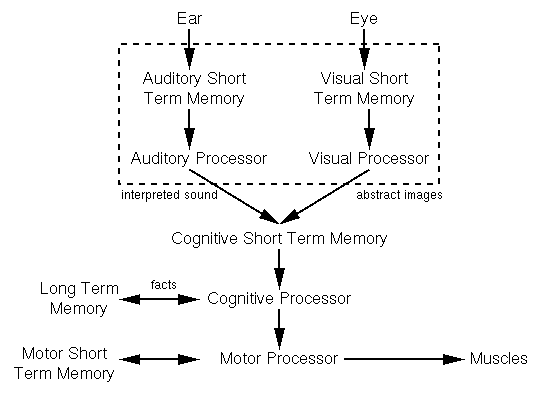
Model Human Processor
GOMS is in fact a family of TA methods:
Natural goals may be related to device-independent goals.
Often defined by hardware.
Methods are used to accomplish goals and are composed of operators.
Mental operators allow sub-goals - hierarchical decomposition.
Describing methods is the focus of task analysis.
Selection rules are needed if there is more than one method for a goal.
Common approach is to convert a general goal in a specific context into a specific goal.
Natural GOMS Language - Kieras, 1988
David Kieras has written a guide to GOMS (and NGOMSL in particular) which is available at: <URL:ftp://ftp.eecs.umich.edu/people/kieras/Guide.ps>
Method for goal: make tea
Step 1. Accomplish goal: boil water
Step 2. Decide: If Verify that pot is full
Then empty pot
Step 3. put leaves in pot
Step 4. pour water
Step 5. Wait for tea to brew
Step 6. pour tea
Selection rule set for goal: boil water
If kettle is electric
Then Accomplish goal: boil-water-in-kettle
Else Accomplish goal: boil-water-on-stove
Return with goal accomplished
Method for goal: boil-water-in-kettle
Step 1. fill kettle
Step 2. turn kettle on
Step 3. Wait for water to boil
Step 4. Return with goal accomplished
Method for goal: boil-water-on-stove
Step 1. fill kettle
Step 2. light stove
Step 3. put kettle on stove
Step 4. Wait for water to boil
Step 5. turn stove off
Step 6. Return with goal accomplished
Tea-making NGOMSL Example
Common architecture in symbolic AI
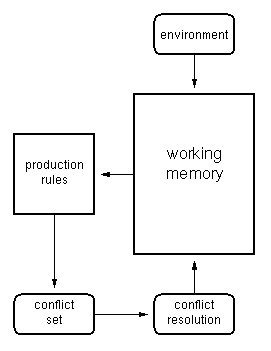
Production Rule System
Working memory contains facts. Production rules are matched against the contents of the WM. Those that match form the conflict set. The process of conflict resolution selects a rule from the conflict set which is then fired, adding new facts to the WM.
GOMS is partly based on earlier work with Production Rule Systems
The correspondence between PS concepts and GOMS concepts is straightforward:
Analyse the task of making a telephone call from a public telephone. Call payment may be in cash, or by credit card, phone card or reverse charges.
$Date: 1999-02-25 12:31:15+00 $