4 minutes
What Exactly happens when you press the power button on PC ?
Operating system is defined as the low-level software that supports a computer’s basic functions,such as scheduling tasks and controlling…
Operating system is defined as the low-level software that supports a computer’s basic functions,such as scheduling tasks and controlling peripherals. OS holds down these 6 high level stages of a typical Linux boot process.
It has a few components that comes into play when you click Power Button
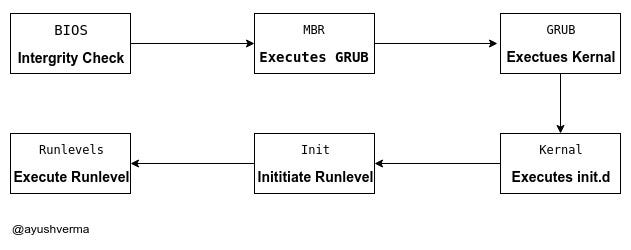 Booting Process Diagram
Booting Process Diagram
1. BIOS
- BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System
- Performs some system integrity checks over the HDD
- Searches, loads, and executes the boot loader program , mostly in MBR
- It looks for boot loader in floppy, cd-rom, or hard drive. We can press a key (typically F12 of F2, but it depends on your system) during the BIOS startup to change the boot sequence.
- Once the boot loader program is detected and loaded into the memory, BIOS gives the control to it.
- So, in simple terms BIOS loads and executes the MBR boot loader.
2. MBR
- MBR stands for Master Boot Record.
- It is located in the 1st sector of the bootable disk. Typically /dev/hda, or /dev/sda. Why it’s sda and hda ? refer here for more.
- MBR is less than 512 bytes in size. This has three components 1) primary boot loader info in 1st 446 bytes 2) partition table info in next 64 bytes 3) mbr validation check in last 2 bytes.
- It contains information about GRUB (or LILO in old systems).
- So, in simple terms MBR loads and executes the GRUB boot loader.
3. GRUB
- GRUB stands for Grand Unified Bootloader.
- If you have multiple kernel images installed on your system, you can choose which one to be executed, by default only the major one boots up .
- GRUB displays a splash screen, waits for few seconds, if you don’t enter anything, it loads the default kernel image as specified in the grub configuration file.
- GRUB has the knowledge of the filesystem (the older Linux loader LILO didn’t understand filesystem).
- Grub configuration file is /boot/grub/grub.conf (/etc/grub.conf is a link to this). The following is sample grub.conf of CentOS.
4. Kernel
- Mounts the root file system as specified in the “root=” in grub.conf
- Kernel executes the /sbin/init program
- Since init was the 1st program to be executed by Linux Kernel, it has the process id (PID) of 1. Do a ‘ps -ef | grep init’ and check the pid. You can also use netstat
- initrd stands for Initial RAM Disk.
- initrd is used by kernel as temporary root file system until kernel is booted and the real root file system is mounted. It also contains necessary drivers compiled inside, which helps it to access the hard drive partitions, and other hardware.
5. Init
- Looks at the /etc/inittab file to decide the Linux run level.
- Following are the available run levels
- 0 — halt
- 1 — Single user mode
- 2 — Multiuser, without NFS
- 3 — Full multiuser mode
- 4 — unused
- 5 — X11
- 6 — reboot
- Init identifies the default initlevel from /etc/inittab and uses that to load all appropriate program.
- Execute ‘grep initdefault /etc/inittab’ on your system to identify the default run level
- If you want to get into trouble, you can set the default run level to 0 or 6. Since you know what 0 and 6 means, probably you might not do that.
- Typically you would set the default run level to either 3 or 5.
 Configuration files present in the init folder
Configuration files present in the init folder
6. Runlevel programs
- When the Linux system is booting up, you might see various services getting started. For example, it might say “starting sendmail …. OK”. Those are the runlevel programs, executed from the run level directory as defined by your run level.
- Depending on your default init level setting, the system will execute the programs from one of the following directories.
- Run level 0 — /etc/rc.d/rc0.d/
- Run level 1 — /etc/rc.d/rc1.d/
- Run level 2 — /etc/rc.d/rc2.d/
- Run level 3 — /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/
- Run level 4 — /etc/rc.d/rc4.d/
- Run level 5 — /etc/rc.d/rc5.d/
- Run level 6 — /etc/rc.d/rc6.d/
By Ayush Verma on October 12, 2017.
Exported from Medium on July 6, 2019.
691 Words
2017-06-09 00:00 +0000